Double
CS2350 bipotentiostat has two sets of built-in independent potentiostat /galvanostat. Experiments can be conducted simul
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | CS2350M |
| Type | Measurement Type |
| Applications | Rrde, Battery, Materials, Corrosion etc |
| Eis Frequency | 10μHz~1MHz |
| Weight | 7kg |
| Power Supply | AC 110V~240V, 50/60Hz |
| Support | We1, We2, CE, Re / We1, Re1, CE1 & We2, Re2, CE2 |
| Number of Channels | 2 |
| Potential Range | ±10V |
| Max. Current Output | ±2A |
| Transport Package | Carton |
| Specification | 36x30x16CM |
| Trademark | Corrtest |
| Origin | China |
| HS Code | 9027899090 |
| Production Capacity | 1000 Sets/Year |
Product Description
CS2350 bipotentiostat has two sets of built-in independent potentiostat /galvanostat. Experiments can be conducted simultaneously in each channel. Besides this, the two channels can jointly complete experiment of two-working electrode system such as RRDE and HDT. CS2350 bipotentiostat is the real double-channel potentiostat. It uses Ethernet connection. The customer can choose to use only one channel or both channels during experiment. EIS function is included in the first channel.
Applications
(1) Electrosythesis, electrodeposition (electroplating), anodic oxidation, electrolysis (2) Oxygen reduction reaction(ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), Hydrogen evolution reaction(HER), carbon dioxide reduction.(3) Energy and materials (Li-ion battery, solar cell, fuel cell, supercapacitor), advanced function materials, and sensor.(4) Corrosion behavior of metals, and anti-corrosion evaluation(5) Fast evaluation of inhibitor, water quality stabilizer, coating, and cathodic protection efficiency.
Standard SupplyInstrument host CS2350 x1CS studio software package x1Power cable x1,Ethernet cable x1,Cell cable x 4Dummy cell (1kΩ||100µF) x2Manual x1Warranty cardx1Service (**All the after service is FREE)Warranty period: 5 years.Provide installation guide, manual, software installation video, and training videos. Lifetime free software upgrading of the same model and technical service.Free repair service
Typical applications for the bipotentiostat
Rotating ring-disk electrode(RRDE)Oxidation/reduction reaction (ORR) study: while measuring the polarization curve of disk electrode in the main channel, apply a constant polarization potential on the ring electrode, and detect the intermediate products on the disk electrode. RRDE test becomes the typical method for ORR study.
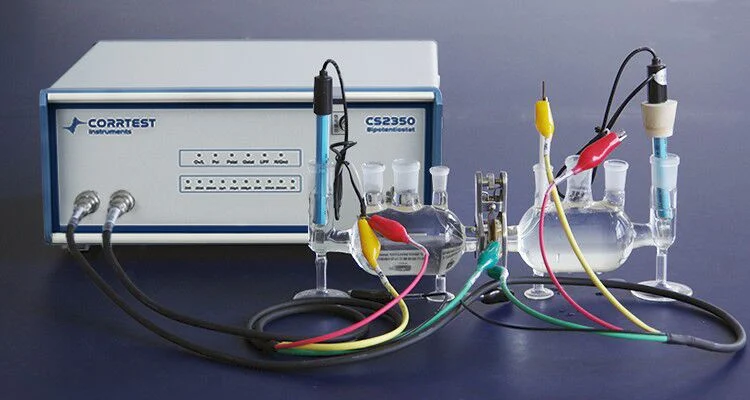
Hydrogen diffusion test (HDT)CS2350 2 channel potentiostat is combined with H cells. For each cell, there is a set of reference &counter electrode, and they share a working electrode which is a thin metal plate clipped in the middle of the two cells. (See the right picture). By measuring current of cathode hydrogen charging (the left cell) and hydrogen atoms anode oxidation (the right cell), it can further calculate the diffusion coefficient of hydrogen atoms in metal and hydrogen flux.

Specifications
| Specifications | |
| Support 2-, 3- or 4-electrode system | Interface: Ethernet |
| Potential control range: Primary Channel: ±10Vsecond Channel: ±10V | Current control range: ±2A |
| Potential control accuracy: 0.1%×full range±1mV | Current control accuracy: 0.1%×full range |
| Potential resolution: 10μV (>100Hz),3μV (<10Hz) | Current sensitivity:1pA |
| Rise time: <1μS (<10mA), <10μS (<2A) | Reference electrode input impedance:1012Ω||20pF |
| Current range: 2nA~2A, 10 ranges | Compliance voltage: ±21V |
| Maximum current output: 2A | CV and LSV scan rate: 0.001mV~10,000V/s |
| CA and CC pulse width: 0.0001~65,000s | Current increment during scan: [email protected]/ms |
| Potential increment during scan: [email protected]/ms | SWV frequency: 0.001~100 kHz |
| DPV and NPV pulse width: 0.0001~1000s | AD data acquisition:[email protected] MHz,[email protected] kHz |
| DA Resolution:16bit, setup time:1μs | Minimum potential increment in CV: 0.075mV |
| IMP frequency: 10μHz~1MHz | Low-pass filters: Covering 8-decade |
| Potential and current range: Automatic | Weight / Measurements: 8kg,36.5 x 30.5 x16cm |
| Operating System: Windows 2000/NT/XP/ win7/win8/win10 | |
| Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy(EIS) | |
| Signal generator | |
| Frequency range:10μHz~1MHz | AC amplitude:1mV~2500mV |
| DC Bias:-10~+10V | Output impedance:50Ω |
| Waveform: sine wave, triangular wave and square wave | Wave distortion:<1% |
| Scanning mode: logarithmic/linear, increase/decrease | |
| Signal analyzer | |
| Integral time:minimum:10ms or the longest time of a cycle | Maximum:106 cycles or 105s |
| Measurement delay:0~105s | |
| DC offset compensation | |
| Potential automatic compensation range:-10V~+10V | Current compensation range:-1A~+1A |
| Bandwidth: 8-decade frequency range, automatic and manual setting | |
Software-Techniques/Methods of CS2350
Channel 1
Stable polarization
- Open Circuit Potential (OCP)
- Potentiostatic (I-T curve)
- Galvanostatic
- Potentiodynamic (Tafel plot)
- Galvanodynamic (DGP)
- Sweep-Step Functions (SSF)
- Multi Potential Steps
- Multi Current Steps
- Potential Stair-Step (VSTEP)
- Galvanic Stair-Step (ISTEP)
- Chronopotentiometry (CP)
- Chronoamperametry (CA)
- Chronocaulometry (CC)
- Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV)
- Cylic Voltammetry (CV)
- Staircase Voltammetry (SCV)
- Square Wave Voltammetry (SWV)
- Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV)
- Normal Pulse Voltammetry (NPV)#
- Differential Normal Pulse Voltammetry (DNPV)
- AC Voltammetry (ACV)
- 2nd harmonic AC Voltammetry (SHACV)
- Fourier Transform AC Voltammetry (FTACV)
- Differential Pulse Amperometry (DPA)
- Double Differential Pulse Amperometry (DDPA)
- Triple Pulse Amperometry (TPA)
- Integrated Pulse Amperometric Detection (IPAD)
- Potentiostatic Stripping
- Linear Stripping
- Staircase Stripping
- Square Wave Stripping
- Differential Pulse Voltammetry Stripping
- Normal Pulse Voltammetry Stripping
- Differential Normal Pulse Voltammetry Stripping
- EIS vs Frequency (IMP)
- EIS vs Time (IMPT)
- EIS vs Potential (IMPE)(Mott-Schottky)
- Cyclic polarization curve (CPP)
- Linear polarization curve (LPR)
- Electrochemical Potentiokinetic Reactivation (EPR)
- Electrochemical Noise (EN)
- Zero resistance Ammeter (ZRA)
- Battery Charge and Discharge
- Galvanostatic Charge and Discharge (GCD)
- Potentiostatic Charging and Discharging
- Potentiostatic Intermittent Titration Technique
- Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique
- Data Logger
- Electrochemical Stripping/ Deposition
- Bulk Eletrolysis with Coulometry (BE)
- Rs Measurement
- Open Circuit Potential (OCP)
- Potentiostatic (I-T curve)
- Galvanostatic
- Potentiodynamic (Tafel plot)
- Galvanodynamic (DGP)
- Sweep-Step Functions (SSF)
- Multi Potential Steps
- Multi Current Steps
- Potential Stair-Step (VSTEP)
- Galvanic Stair-Step (ISTEP)
- Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV)
- Cylic Voltammetry (CV)
- Cyclic polarization curve (CPP)
- Linear polarization curve (LPR)
- Electrochemical Potentiokinetic Reactivation (EPR)
- Electrochemical Noise (EN)
- Zero resistance Ammeter (ZRA)
- Battery Charge and Discharge
- Galvanostatic Charge and Discharge (GCD)
- Potentiostatic Charging and Discharging
- Potentiostatic Intermittent Titration Technique
- Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique
- Data Logger
- Electrochemical Stripping/ Deposition
- Bulk Eletrolysis with Coulometry (BE)
- Rs Measurement
Send to us






